Vitamin B2, also known as Riboflavin or Vitamin G, is an essential nutrient required for proper energy production, healthy skin, eyes, nerves, and digestion. Deficiency of Vitamin B2 can lead to several health problems affecting multiple systems of the body.
In this article, we will discuss Vitamin B2 deficiency symptoms, diseases, food sources, dosage, and important facts in detail.
What is Vitamin B2 (Riboflavin)?
Vitamin B2 is a water-soluble vitamin that plays a vital role in:
- Energy metabolism
- Cell growth and repair
- Healthy skin, eyes, and nervous system
- Conversion of carbohydrates into energy
Scientifically, Vitamin B2 is also known as Lactoflavin.
Diseases & Symptoms Caused by Vitamin B2 Deficiency
When the body lacks Vitamin B2, the following symptoms and health disorders may appear:
Digestive Problems
- Constipation
- Indigestion
- Poor digestion
- Stomach cramps
- Intestinal gas
- Chronic dysentery
- Duodenal disorders
- Liver disorders
- Hepatitis
- Liver abscess
Skin & Hair Problems
- Dry and rough skin
- Red, pus-filled pimples
- Boils and infected wounds
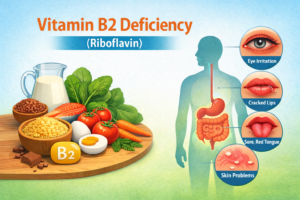
- Cracking of lips (cheilosis)
- Peeling of skin
- Premature greying of hair
- Acne and skin inflammation
Mouth, Tongue & Nose Disorders
- Cracks at the corners of the mouth
- Mouth ulcers
- Red, swollen, and thick tongue
- Burning sensation in the mouth
- Swelling and infection of the nose
- Thickening of mucous membranes
Eye Problems
- Burning sensation in the eyes
- Blurred vision
- Excessive tearing
- Conjunctivitis
- Dry eyes
- Eyelid irritation and itching
- Corneal inflammation
- Swelling of the eyes
One of the most prominent signs of Vitamin B2 deficiency is cracking and yellowish discoloration at the corners of the lips.
Nervous System & General Weakness
- Nerve weakness
- Headache
- Spinal degeneration (in severe deficiency)
- General body weakness
- Pregnancy weakness
- Post-delivery weakness
- Breastfeeding weakness
- Children not gaining weight properly
Genital & Itching Problems
- Vaginal itching in women
- Itching near the testicles
- Itching around the nose and ears
- Itchy wounds and boils
Important Facts About Vitamin B2
- Vitamin B2 is yellow in color
- It is less soluble in water
- It gets destroyed when mixed with sodium bicarbonate (baking soda)
- Excess Vitamin B2 is excreted through urine
- Deficiency of Vitamin B1 and B2 often occurs together
- Deficiency of one B-complex vitamin usually means deficiency of others
- Diseases of the tongue and lips are commonly linked to Vitamin B2 deficiency
- Distal nerve disorders may occur due to deficiency
Recommended Daily Dose of Vitamin B2
| Person Type | Daily Requirement |
|---|---|
| Healthy Adult | 1–3 mg |
| Deficiency Patient | Up to 50 mg (as advised by a healthcare professional) |
⚠️ High doses should be taken only under medical supervision.
Foods Rich in Vitamin B2 (Riboflavin)
Here is a table of natural food sources of Vitamin B2:
- Milk
- Fish
- Eggs (especially egg whites)
- Liver
- Yeast
- Wheat germ
- Rice bran
- Tomatoes
- Carrots
- Cabbage
- Beans
- Asava & Arista
- Sprouts
- Green leafy vegetables
Vitamin B2 Deficiency Treatment
- Mild deficiency can be corrected by dietary changes
- Moderate to severe deficiency may require Vitamin B2 supplements
- Vitamin B2 supplementation often helps relieve symptoms without additional medication, when deficiency is the root cause
Conclusion
Vitamin B2 (Riboflavin) is a crucial nutrient for maintaining healthy digestion, skin, eyes, nerves, and energy levels. Deficiency can lead to multiple health issues, but timely identification and proper intake can restore health effectively.
⚠️ Medical Disclaimer
This article is for educational purposes only. Vitamin deficiencies and related symptoms should be evaluated by a qualified healthcare professional before starting any supplementation.
Also read this post :- What is vitamin B1 (thiamine hydrochloride)?
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ) – Vitamin B2 Deficiency
Vitamin B2 deficiency occurs when the body does not get enough Riboflavin, an essential vitamin required for energy production, healthy skin, eyes, digestion, and nervous system.
Common symptoms include cracked lips, mouth ulcers, red and swollen tongue, blurred vision, eye irritation, dry skin, pimples, nerve weakness, headache, and digestive problems like indigestion and constipation.
Vitamin B2 deficiency can cause digestive disorders, skin diseases, eye problems (conjunctivitis, corneal inflammation), anemia, liver disorders, nerve weakness, mouth and tongue diseases, and general body weakness.
The most prominent sign is cracking and yellowish discoloration at the corners of the mouth, along with burning and itching sensation.
Yes, deficiency of Vitamin B2 can cause blurred vision, burning eyes, excessive tearing, dry eyes, conjunctivitis, and corneal inflammation.
Vitamin B2 is found in milk, fish, eggs, liver, yeast, wheat germ, rice bran, tomatoes, carrots, cabbage, beans, and green leafy vegetables.
A healthy adult requires 1–3 mg per day, while a person suffering from deficiency may need up to 50 mg daily, as advised by a doctor.
Mild deficiency can be corrected through a Vitamin B2-rich diet, but moderate or severe deficiency may require supplements.
No, excess Vitamin B2 is generally safe as it is excreted from the body through urine.
Usually not. Deficiency of Vitamin B2 often occurs along with other Vitamin B-complex deficiencies.
Yes, it can cause dry skin, pimples, acne, boils, itching, infected wounds, and cracked lips.
