What is a Stroke?
A stroke is a serious medical emergency that occurs when the blood supply to the brain is interrupted or reduced. This prevents brain tissue from receiving oxygen and nutrients, causing brain cells to begin dying within minutes. Immediate medical attention is critical to reduce brain damage and improve survival chances.
Stroke is one of the leading causes of death and long-term disability worldwide. Understanding its types, causes, and warning signs can help save lives.
Types of Stroke
There are three main types of stroke:
- Ischemic Stroke
- Hemorrhagic Stroke
- Transient Ischemic Attack (TIA)
Each type has different causes and effects on the brain.
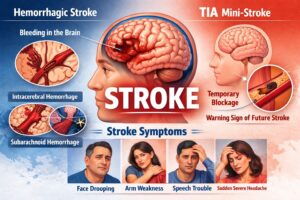
Hemorrhagic Stroke
A hemorrhagic stroke occurs when a blood vessel in the brain leaks or ruptures. The leaking blood puts pressure on brain tissues, damaging brain cells and affecting brain function.
This type of stroke is often caused by:
- High blood pressure (hypertension)
- Head trauma or injury
- Weak blood vessels (aneurysm)
- Blood-thinning medications such as heparin
- Abnormal blood vessels
Types of Hemorrhagic Stroke
1. Intracerebral Hemorrhage
This is the most common type of hemorrhagic stroke. It occurs when a blood vessel bursts inside the brain, causing bleeding within brain tissue.
2. Subarachnoid Hemorrhage
This is less common but very serious. It occurs when bleeding happens in the space between the brain and the thin protective tissues covering the brain, known as the subarachnoid space.
Transient Ischemic Attack (TIA)
A Transient Ischemic Attack (TIA), also known as a “mini-stroke,” occurs when blood flow to the brain is temporarily blocked. Unlike other strokes, the blockage lasts only a short time and does not cause permanent brain damage.
TIAs are usually caused by small blood clots in brain arteries.
Even though symptoms may disappear quickly, TIAs are extremely dangerous warning signs. Studies show that many patients who experience a TIA suffer a major stroke within one year if proper treatment and preventive measures are not taken.
TIA should always be treated as a medical emergency.
Common Stroke Symptoms
Recognizing stroke symptoms early can save lives. Common symptoms include:
- Sudden weakness or numbness in the face, arm, or leg (especially on one side of the body)
- Difficulty speaking or understanding speech
- Sudden confusion
- Loss of balance or coordination
- Severe headache with no known cause
- Vision problems in one or both eyes
Use the FAST method to identify stroke quickly:
- F – Face drooping
- A – Arm weakness
- S – Speech difficulty
- T – Time to call emergency services
Causes and Risk Factors of Stroke
Several factors increase stroke risk, including:
- High blood pressure
- Smoking
- Diabetes
- High cholesterol
- Obesity
- Heart disease
- Sedentary lifestyle
- Excessive alcohol consumption
- Blood clotting disorders
Stroke Prevention Tips
You can reduce your stroke risk by following these healthy habits:
- Maintain healthy blood pressure
- Exercise regularly
- Eat a balanced and healthy diet
- Quit smoking
- Limit alcohol consumption
- Control diabetes and cholesterol
- Maintain a healthy weight
- Take prescribed medications regularly
When to See a Doctor
Stroke is a life-threatening emergency. If you or someone nearby shows stroke symptoms, seek immediate medical help. Early treatment can prevent severe brain damage, disability, or death.
Conclusion
Stroke is a serious condition that requires immediate medical attention. Hemorrhagic stroke occurs due to bleeding in the brain, while TIA is a temporary blockage that serves as a warning sign for future strokes. Understanding stroke symptoms, causes, and prevention methods can help reduce risks and save lives.
Early diagnosis and timely treatment are the key to recovery and prevention.
